Here at our expert machine vision lens guide, we provide the necessary insights to help you make the right choice.
With a plethora of options available, selecting the most suitable lens for your application can be challenging. We delve into the intricacies of different lens types, such as c-mount and CS mount lenses, and explore focal length, aperture, and the innovative liquid lens technology.
By the end, you’ll be equipped with the knowledge needed to confidently choose the ideal machine vision lens.

The Importance of the Lens in Machine Vision
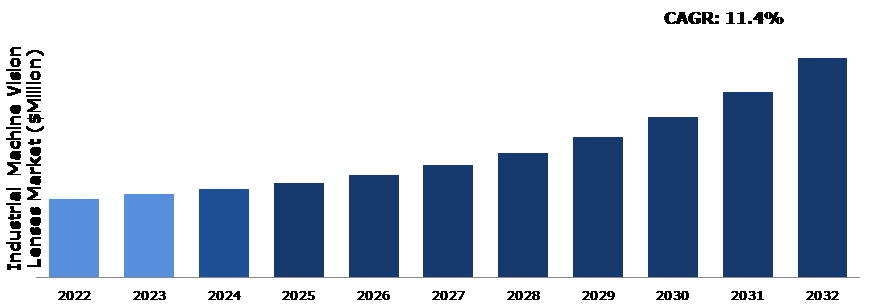
According to Research Dive report the industrial machine vision lenses market is predicted to grow with a CAGR of 11.4% and generate a revenue of $19,939.40 million by 2032.
When it comes to machine vision, the lens plays a crucial role in capturing accurate and high-quality images. The lens determines factors such as focal length, working distance, and aperture, which directly impact the clarity and depth of field of the images.
Therefore, selecting the right lens is essential for ensuring the success and reliability of machine vision applications.
Factors to Consider When Selecting a Machine Vision Lens
One important factor to consider when selecting a machine vision lens is the focal length, as it determines the focus and magnification of the inspection object. The focal length of the lens determines the distance between the lens and the image sensor, which affects image quality.
The appropriate focal length depends on the application and the desired field of view. In industrial machine vision applications, it’s crucial to choose a lens with a focal length that matches the sensor size of the camera.
Additionally, the working distance, which is the distance between the lens and the inspection object, should also be taken into account. The lens should be able to maintain sharp focus at the desired working distance to ensure accurate inspection results.
Types of Machine Vision Lenses
When considering the types of machine vision lenses, it’s important to understand the different options available.
Prime lenses offer a fixed focal length and are commonly used when the object is always at a set distance from the camera.
Macro lenses are designed for close-up imaging, while telecentric lenses provide accurate measurements and minimal distortion.
Vibration-resistant lenses are ideal for applications with high levels of vibration, while wide-angle lenses offer a larger field of view.
Prime Lenses
We can consider prime lenses as a versatile option for machine vision applications. Prime lenses have a fixed focal length, meaning they do not have the ability to zoom in or out.
However, they offer excellent image quality and are often chosen for their sharpness and low distortion.
When choosing the right lens for your machine vision application, it is important to consider the specific requirements of your application.
The table below provides a comparison of prime lenses based on their focal length, aperture, and suitability for different machine vision applications.
| Prime Lens | Focal Length (mm) | Aperture | Suitable Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lens A | 16 | f/1.8 | High-speed imaging |
| Lens B | 35 | f/2.8 | Object recognition |
| Lens C | 50 | f/1.4 | Inspection |
| Lens D | 85 | f/1.2 | Surveillance |
| Lens E | 100 | f/2.0 | Robotics |
Macro
There are two common types of macro lenses available for machine vision applications: fixed macro lenses and variable macro lenses.
Fixed macro lenses:
– These lenses have a fixed focal length and are used when the object being inspected is always at a set distance from the camera.
– They provide consistent magnification and are ideal for applications where the object size and working distance remain constant.
– Fixed macro lenses offer high resolution and accuracy, making them suitable for precise inspection tasks.
Variable macro lenses:
– These lenses have a variable focal length, allowing for quick adjustments to focus.
– They provide flexibility in inspecting objects of varying sizes and working distances.
– Variable macro lenses are often used in applications where the object size and working distance can change, requiring the ability to adapt quickly.
Both types of macro lenses can be used with c-mount lenses, which are commonly used in machine vision systems. It’s important to consider the object size, working distance, and illumination requirements when selecting the appropriate macro lens for your vision system.
Telecentric
As we explore the topic of telecentric lenses in machine vision, it’s important to understand their unique characteristics and applications.
Telecentric lenses are a type of lens used in machine vision applications where accuracy and precision are crucial. Unlike conventional lenses, telecentric lenses have a unique optical design that ensures that the light rays are parallel to the optical axis, resulting in minimal distortion and accurate measurements.
This makes telecentric lenses ideal for applications such as metrology, inspection, and measurement in industries like automotive and manufacturing.
When choosing the right telecentric lens for your application, it’s essential to consider factors such as the working distance, field of view, and resolution requirements.
It’s also important to select a reputable lens manufacturer that offers a wide range of options to meet your specific needs.
Vibration resistant
When considering vibration resistant lenses for machine vision applications, it’s important to choose a lens that can withstand the vibrations present in the environment. Here are three key factors to consider when selecting a vibration resistant lens for your application:
Lens design:
Look for lenses that are specifically designed for use in machine vision applications where vibration is a concern. These lenses often have reinforced components and shock-absorbing mechanisms to minimize the impact of vibrations on image quality.
Camera compatibility:
Ensure that the lens is compatible with your camera system. Different industrial cameras may have different mounting options and connection interfaces, so it’s important to choose a lens that can be easily integrated.
Shutter speed:
Consider the shutter speed that your application requires. High-speed vibrations may require a lens with a fast shutter speed to capture clear images without motion blur.
Wide angle
We recommend considering the use of a wide-angle lens for your machine vision application, as it can capture a larger field of view and provide a broader perspective.
Wide-angle lenses have a shorter focal length, typically less than 35mm, allowing them to capture a wider area compared to standard or telephoto lenses. This is particularly useful when you need to monitor a large space or capture multiple objects within the frame.
Wide-angle lenses are commonly used in applications such as surveillance, robotics, and quality inspection, where a comprehensive view is essential.
However, it’s important to note that wide-angle lenses can introduce distortion and reduced image resolution towards the edges of the frame. Therefore, it’s crucial to select a high-quality wide-angle lens that can minimize these effects and deliver accurate and clear images for your machine vision system.
Connection Types
Exploring different connection types is essential when selecting the right machine vision lens for our application. The connection type determines how the lens attaches to the camera, and it plays a crucial role in ensuring compatibility and functionality.

There are several connection types commonly used in machine vision, including C-mount, CS-mount, M42, and F-mount.
C-mount lenses have a 1-inch diameter and 32 threads per inch. The distance between the rear of the lens and the image sensor is 0.69 inches.
CS-mount lenses are similar to C-mount lenses but have a shorter distance of 12.5 millimeters. However, C-mount lenses can be used on CS-mount cameras with a 5 millimeter extension tube.
When choosing a connection type, it’s important to consider the camera and lens compatibility, as well as the required distance between the lens and the image sensor.
Understanding the different connection types available will help us make an informed decision and select the right machine vision lens for our specific application.
Lens Aperture and Focus
When considering lens aperture and focus for our machine vision application, it’s important to understand the impact of these factors on image quality and depth of field. Here are three key points to consider:
Aperture:
The aperture setting determines the amount of light that enters the lens. A wider aperture allows more light to pass through, resulting in a brighter image. However, a wider aperture also decreases the depth of field, making it more challenging to keep all objects in focus. On the other hand, a narrower aperture increases the depth of field but may require longer exposure times or additional lighting.
Focus:
Achieving sharp focus is crucial for accurate machine vision applications. The focus point determines the distance at which objects appear sharp in the image. It’s important to select a lens with a suitable focal length and focusing mechanism that can achieve the desired level of detail and clarity.
Depth of Field:
The depth of field refers to the range of distances over which objects appear acceptably sharp in the image. It’s influenced by the aperture setting, focal length, and distance between the lens and the object. Understanding the depth of field is essential for ensuring that all critical features in the field of view are in focus.
How to Choose the Right Lens?
When choosing the right lens for your machine vision application, there are several points to consider.
First, it’s important to understand the specific requirements of your application, including factors such as lighting conditions, object size, and desired level of detail.
Next, considering the field of view and working distance will help determine the appropriate focal length for the lens.
Additionally, matching the lens to the camera sensor is crucial to ensure compatibility and optimal image quality.
Lastly, assessing the lens’ optical quality, including factors such as resolution, distortion, and chromatic aberration, will help ensure accurate and reliable machine vision performance.
Understanding Your Application’s Requirements
As we delve into understanding our application’s requirements, it’s important to consider various factors when choosing the right lens for our machine vision system.
Here are three key considerations to help guide our decision-making process:
Field of view:
We need to determine the desired field of view for our application, which is the area of the scene that the lens can capture. This will depend on the size of the objects we want to inspect and the distance between the camera and the objects.
Working distance:
The working distance is the distance between the lens and the objects being inspected. It’s crucial to choose a lens with the appropriate working distance to ensure accurate focus and image quality.
Resolution requirements:
The resolution requirements of our application will determine the minimum level of detail that our lens needs to capture. This will depend on factors such as the size of the objects and the level of precision required for inspection.
Considering Field of View and Working Distance
To determine the appropriate lens for our machine vision system, we need to consider both the field of view and working distance.
The field of view refers to the area that the lens can capture, while the working distance is the distance between the lens and the object being inspected. These two factors are crucial in selecting the right lens because they determine the amount of detail that can be captured and the size of the object that can be inspected.
A larger field of view allows for a wider area to be captured, while a shorter working distance is ideal for smaller objects that require close inspection. On the other hand, a smaller field of view is suitable for capturing fine details, while a longer working distance is necessary for larger objects.
Matching the Lens to the Camera Sensor
We have several factors to consider when matching the lens to the camera sensor in order to choose the right lens for our machine vision system. These factors include:
Sensor Size:
The lens must be compatible with the size of the camera sensor to ensure proper image capture and resolution.
Focal Length:
The focal length of the lens determines the field of view and the magnification of the image. It should be selected based on the desired inspection area and object size.
Lens Mount:
The lens mount should match the camera’s mount to ensure a secure and stable connection.
Assessing The Lens’ Optical Quality
By carefully evaluating the lens’ optical quality, we can determine the right lens for our machine vision application. When assessing the optical quality of a lens, there are several important factors to consider.
These include resolution, distortion, vignetting, and chromatic aberration. Resolution refers to the ability of the lens to accurately capture fine details.
Distortion refers to any deviation from a straight line, which can affect the accuracy of measurements.
Vignetting is the darkening of the image towards the edges, which can impact the uniformity of illumination.
Chromatic aberration is the color fringing that can occur, especially at the edges of the image.
To help understand these factors, the following table provides a visual representation:
| Optical Quality | Factors to Consider |
|---|---|
| Resolution | – MTF (Modulation Transfer Function) |
| – Pixel Size | |
| Distortion | – Barrel Distortion |
| – Pincushion Distortion | |
| Vignetting | – Illumination Fall-off |
| Chromatic Aberration | – Lateral Chromatic Aberration |
| – Longitudinal Chromatic Aberration |
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Choosing a Machine Vision Lens
When choosing a machine vision lens, it’s crucial not to overlook its importance in the overall system. Failure to consider environmental factors can lead to suboptimal performance and potential damage to the lens.
Additionally, not accounting for resolution and image quality requirements can result in inadequate image capture and analysis.
Overlooking the Importance of the Lens in the System
One common mistake to avoid when choosing a machine vision lens is overlooking the importance of the lens in the system. Here are three key reasons why the lens is crucial in machine vision applications:
Optimal Image Quality:
The lens plays a critical role in capturing high-quality images. It determines factors such as resolution, distortion, and color accuracy. Choosing the right lens ensures that the system can accurately analyze the images and make precise decisions.
Proper Field of View:
The lens determines the field of view, which is the area that the camera can capture. It’s essential to select a lens with the appropriate focal length to ensure that the desired area is covered and the necessary details are captured.
Compatibility with Camera and Lighting:
The lens must be compatible with the camera and lighting setup to achieve optimal performance. Consider factors such as lens mount type, sensor size, and working distance to ensure seamless integration with the rest of the system.
Failure to Consider Environmental Factors
In our experience, we often fail to consider environmental factors when choosing a machine vision lens. This oversight can lead to significant problems in the performance and longevity of the lens.
Environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and dust can have a detrimental effect on the lens and ultimately impact the accuracy and reliability of the machine vision system. Extreme temperatures can cause lens distortion or affect the internal components, while high levels of humidity can lead to condensation and fogging inside the lens.
Additionally, dust particles can accumulate on the lens surface, leading to reduced image quality and potentially damaging the lens. Therefore, it’s crucial to thoroughly assess the environmental conditions in which the machine vision system will operate and choose a lens that’s specifically designed to withstand those conditions.
Not Accounting for Resolution and Image Quality
Have we considered the resolution and image quality when choosing a machine vision lens? It’s crucial to take these factors into account to ensure accurate and reliable results. Here are some common mistakes to avoid:
Neglecting resolution requirements:
– Failing to match the lens resolution with the camera’s sensor resolution can result in decreased image quality and loss of important details.
– Choosing a lens with a lower resolution than required can limit the system’s ability to detect and measure objects accurately.
Ignoring image distortion:
– Lens distortion can affect the accuracy of measurements and lead to incorrect analysis.
– Understanding the lens’s distortion characteristics and selecting one with minimal distortion is essential for precise machine vision applications.
Overlooking lens coating and optical quality:
– Coatings can reduce reflections and improve light transmission, resulting in clearer images.
– Opting for high-quality lenses with superior optics can minimize aberrations and ensure sharper and more accurate images.
Machine Vision Lenses Manufacturers
Machine vision lenses manufacturers play a pivotal role in the rapidly advancing field of industrial automation and quality control.
These specialized companies design and produce precision optics tailored to the needs of machine vision systems, enabling high-resolution imaging, accurate inspections, and enhanced productivity in various industries.
In this list, we highlight some notable manufacturers driving innovation in the world of machine vision optics.1.
- Tamron Co., Ltd.
- Fujifilm Corporation
- Schneider Kreuznach
- Edmund Optics Inc.
- Opto Engineering srl
- Computar Optics Group
- The Imaging Source Europe GmbH
- Zeiss Group
- Kowa Co., Ltd.
- First Sensor AG
Conclusion
We have explored the different types of lenses and their specifications, allowing us to make an informed decision when choosing the right machine vision lens for our application. By understanding the different types of lenses available, such as C-mount and CS-mount lenses, we can select the appropriate lens based on our specific needs.
Additionally, we’ve learned about fixed and variable focal lenses, which provide flexibility in focusing on objects at different distances. The use of liquid lens technology further enhances our options, allowing for quick adjustments in focus without the need for mechanical adjustments.
Furthermore, we’ve gained an understanding of key vision terminology, including focal length, working distance, camera distance, and aperture, which are crucial in determining the focus, magnification, and depth of field of our inspection objects.
Armed with this knowledge, we’re now equipped to choose the right machine vision lens for our application.

