The integration of machine vision in Industry 4.0 has sparked a revolution in efficiency. With its ability to detect faults and identify defects at an accelerated pace, machine vision plays a critical role in quality assurance, enforcement, and inventory management.
By minimizing human error and enabling robots to perceive and assist in dynamic systems, this technology enhances automation and productivity.
As we explore the significant applications, advanced capabilities, and future prospects of machine vision, it becomes clear that it is a key driver of efficiency in Industry 4.0.
What is machine vision and how does it work?
Machine vision is a technology that enables machines to see and interpret images or videos, similar to how human vision works.
It relies on the use of industrial cameras or sensors to capture visual data and then uses algorithms and machine learning techniques to analyze and process the data.
This allows machines to make decisions or carry out tasks based on what they “see” in the physical world.

Machine vision types
Machine vision encompasses various types of technologies and approaches used to enable machines, typically computers, to “see” and interpret visual information from the world around them. Here are some common types of machine vision:
- 2D Vision: This is the most basic form of machine vision, where systems analyze two-dimensional images or video frames to perform tasks such as object detection, pattern recognition, and quality control.
- 3D Vision: 3D machine vision systems capture depth information in addition to 2D data. They are used for tasks like measuring the dimensions of objects, inspecting surface profiles, and navigating in 3D environments.
- Color Vision: Color machine vision systems use color cameras to analyze and process images based on color information. They are valuable in applications where color plays a critical role, such as sorting products by color or inspecting the color of objects.
- Stereo Vision: Stereo vision uses two or more cameras to create a 3D representation of a scene by comparing the differences in the images captured by each camera. This technology is used for depth perception and object tracking.
- Thermal Imaging: Thermal machine vision utilizes infrared cameras to detect and analyze heat signatures. It’s commonly used in applications such as detecting temperature anomalies in industrial processes or identifying warm-blooded animals in surveillance.
- Hyperspectral Imaging: This technology captures a wide range of narrow, contiguous wavelengths of light, allowing for detailed analysis of materials based on their spectral signatures. It is used in agriculture, food inspection, and material analysis.
- Line Scan Imaging: In this approach, a single line sensor captures images of objects as they move along a conveyor belt or production line. It’s useful for inspecting continuous processes and high-speed manufacturing.
- Time-of-Flight (ToF) Imaging: ToF cameras use the time it takes for light or laser pulses to bounce off objects and return to the sensor to measure distances. They are employed for 3D scanning and depth sensing applications.
- Hyper-Resolution Imaging: This technique combines multiple images taken at different focal lengths to create an image with an extended depth of field. It’s useful for capturing sharp images of objects with varying heights.
- Machine Vision with Deep Learning: Deep learning, particularly convolutional neural networks (CNNs), is increasingly integrated into machine vision systems for tasks like object recognition, image classification, and image segmentation.
- Embedded Vision: These are machine vision systems integrated into devices or machines themselves, often using compact, specialized cameras and processing units for real-time analysis.
- Multi-Spectral Imaging: This involves capturing images in multiple spectral bands beyond the visible spectrum, such as ultraviolet or infrared, for applications like material identification or document inspection.
These various types of machine vision technologies are applied across a wide range of industries, including manufacturing, agriculture, healthcare, automotive, and robotics, to automate processes, improve quality control, and enhance decision-making based on visual data.
The Role of Machine Vision in Industry 4.0
Industry 4.0, also known as the fourth industrial revolution, refers to the integration of advanced digital technologies into the manufacturing sector.
It encompasses concepts such as the Internet of Things (IoT), cyber-physical systems, and data analytics. Machine vision plays a crucial role in Industry 4.0 by providing real-time data capture and analysis, enabling factories to make informed decisions and improve their processes.
The impact of machine vision on automation
Automation has been a key driver in increasing productivity and reducing waste in manufacturing. With the use of machine vision, automation systems can be enhanced further.
Machine vision enables machines to “see” and understand their surroundings, allowing them to adapt and make intelligent decisions based on the visual data they receive. This leads to improved efficiency, accuracy, and speed in production lines.
The role of machine vision in the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) refers to the network of connected devices, sensors, and machines in the manufacturing environment.
Machine vision plays a vital role in the IIoT by providing visual data that can be integrated into the larger data ecosystem.
This enables data analytics and real-time monitoring, resulting in actionable insights and continuous improvement in factory utilization and productivity.
Advantages of Machine Vision
Improved quality control and defect detection
Machine vision systems can detect even minor defects or variations in products, ensuring high-quality standards in the manufacturing process. It reduces the risk of human error and enables early identification of potential issues, preventing costly quality-related problems.
Enhanced productivity and efficiency
By automating certain tasks and providing real-time feedback, machine vision improves efficiency in production lines. It allows for faster inspection and sorting of products, reducing bottlenecks and optimizing overall throughput. Labor productivity also sees gains in areas where machine vision is implemented.
Real-time monitoring and data analysis
Machine vision systems provide real-time insights into the production process, enabling immediate action to resolve deviations or issues. They contribute to the generation of big data, which can be further analyzed to identify patterns, optimize workflows, and drive continuous improvement.
Applications of Machine Vision in Industry 4.0
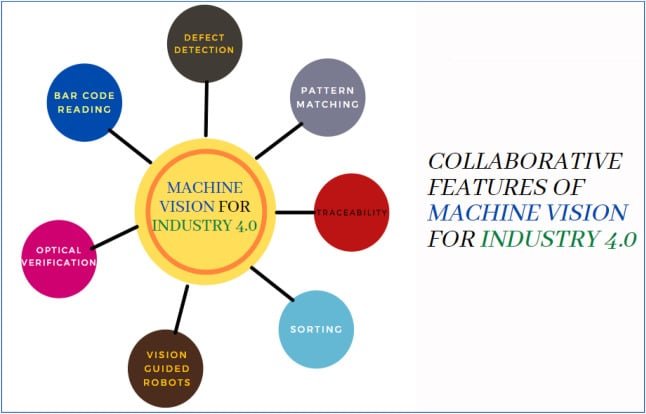
Automated inspection and quality control
Machine vision is widely used in automated inspection processes to ensure product quality and detect any abnormalities or defects. It can detect variations in size, shape, color, or texture, allowing for precise quality control in a wide range of industries.
Robotic guidance and assembly
Machine vision is utilized to guide robots in various assembly processes, where high precision is required. By providing visual feedback, machine vision enables robots to accurately pick and place objects, improving efficiency and reducing errors.
Traceability and identification
Machine vision is used for traceability purposes, by reading barcodes or QR codes to identify products, track their journey through the supply chain, and ensure proper labeling and packaging. This enhances inventory management and reduces the risk of errors or misplacements.
Case Studies
AI Quality Inspection in Medical Device Manufacturing: EasyODM helped a leading medical device manufacturer maintain high-quality standards by implementing machine vision for quality control, ensuring the reliability and safety of their medical products. Read the case study
PET Preforms AI Quality Inspection: EasyODM’s machine vision software improved the quality of PET preforms for a major manufacturer, ensuring consistent color quality while efficiently detecting defects in production. Read the case study
Automated AI Quality Control in Lamella Flooring Manufacture: EasyODM collaborated with a hardwood flooring manufacturer to enhance quality control for solid wood lamellas and parquet, using automated visual inspection software powered by machine vision and AI. Read the case study
Automotive Seats AI Defects Detection: EasyODM’s software played a crucial role in the automotive industry by accurately detecting defects in automotive seats using machine learning, ensuring top-quality seats for one of the largest automotive manufacturers. Read the case study
These case studies demonstrate how EasyODM’s machine vision solutions have been applied across various industries to improve quality control processes, increase efficiency, and reduce production costs. Read the case study
Future Trends and Challenges
Emerging technologies and advancements
As technology continues to advance, machine vision is expected to benefit from emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, deep learning, and edge computing. These advancements will further enhance the capabilities of machine vision systems, allowing for more complex analysis, faster processing, and greater accuracy.
Data privacy and security concerns
With the increased use of machine vision and the integration of data analytics in Industry 4.0, there are concerns surrounding data privacy and security. Protecting sensitive information and ensuring secure data transmission will be crucial to maintain trust and address potential vulnerabilities.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Machine Vision in Industry 4.0?
Machine Vision in Industry 4.0 refers to the use of advanced imaging and analysis technology to automate visual inspection, process control, and quality assurance in the manufacturing industry.
How does Machine Vision enhance automation in the industry?
Machine Vision enhances automation in the industry by using advanced cameras and software to perform tasks that are traditionally done by humans, such as quality control, defect detection, and measurement. This improves efficiency, reduces errors, and increases productivity.
What is the role of Machine Vision in exploring the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)?
Machine Vision plays a crucial role in exploring the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) by providing real-time data and analysis, enabling machines to communicate and work together seamlessly. It integrates with other IIoT systems, enabling smart decision-making and increasing overall productivity.
How is machine vision used in robotic guidance?
Machine Vision is used in robotic guidance to enable robots to perceive their environment and perform tasks with precision. By using cameras and advanced algorithms, robots can locate objects, navigate obstacles, and execute tasks accurately.
How does using machine vision improve labor productivity?
Using machine vision improves labor productivity by automating repetitive and time-consuming tasks. With machine vision systems in place, workers can focus on more complex and value-added activities, leading to increased overall productivity.
What is meant by 3D machine vision with automation?
3D machine vision with automation refers to the use of three-dimensional imaging and analysis technology to automate processes within the manufacturing industry. It allows for accurate spatial perception, object recognition, and dimensional measurement for various applications.
How is machine vision used to identify discrepancies in production processes?
Machine vision is used to identify discrepancies in production processes by analyzing images or video streams of products or components. It can detect defects, variations, or anomalies, ensuring that only products meeting the desired quality standards are released.
How is 3D machine vision incorporated into quality assurance roles?
3D machine vision is incorporated into quality assurance roles by providing detailed and accurate measurements, surface inspection, and defect detection capabilities. It helps ensure consistent quality and reduces the risk of defective products reaching the market.
How has 3D machine vision improved quality control in the manufacturing industry?
3D machine vision has made significant advancements in quality control within the manufacturing industry. Its ability to capture and analyze three-dimensional data enables more precise measurements, accurate inspections, and improved consistency in the manufacturing process.
What is the significance of machine vision in the food industry?
Machine vision plays a critical role in the food industry by ensuring quality, safety, and compliance with regulations. It can identify contamination, detect defects, and monitor packaging integrity, contributing to the overall production and delivery of safe food products.
Conclusion
Machine vision plays a vital role in enhancing automation and driving productivity in Industry 4.0. Its use in quality control, real-time monitoring, and data analysis brings numerous benefits to manufacturing processes, resulting in improved efficiency, accuracy, and overall competitiveness.
As technology continues to evolve, machine vision will continue to thrive in Industry 4.0, shaping the future of automation and revolutionizing the way products are manufactured.
Want Flawless Product Quality?
Book a free strategy call to see how AI-powered inspection can streamline your production.

Gediminas Mickus
Business Development Manager

